Skeletal muscles comprise 30% to 40% of your total body mass. They’re the muscles that connect to your bones and allow you to perform a wide range of movements and functions. Skeletal muscles are voluntary, meaning you control how and when they work. It’s important to keep your skeletal muscles as strong and healthy as possible.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The majority of the muscles in your body are skeletal muscles (striated muscles). They make up between 30% and 40% of your total body mass. Tendons (tough bands of connective tissue) attach skeletal muscle tissue to bones throughout your body. Your shoulder muscles, hamstring muscles and abdominal muscles are all examples of skeletal muscles.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are three types of muscles in your body: skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, meaning you control how and when they move and work. Nerves in your somatic nervous system send signals to make them function. If you reach for a book on a shelf, you’re using skeletal muscles in your neck, arm and shoulder.
Cardiac and smooth muscle are involuntary muscles that your autonomic nervous system controls. That means they work without you having to think about it. For example, muscles in your urinary system help rid your body of waste and toxins.
Skeletal muscle mass varies from person to person. Males have more skeletal muscle mass than females. People who are tall or have overweight also tend to have higher muscle mass. Muscle mass decreases with age.
Your striated muscles are a vital part of your musculoskeletal system. They serve a variety of functions, including:
Advertisement
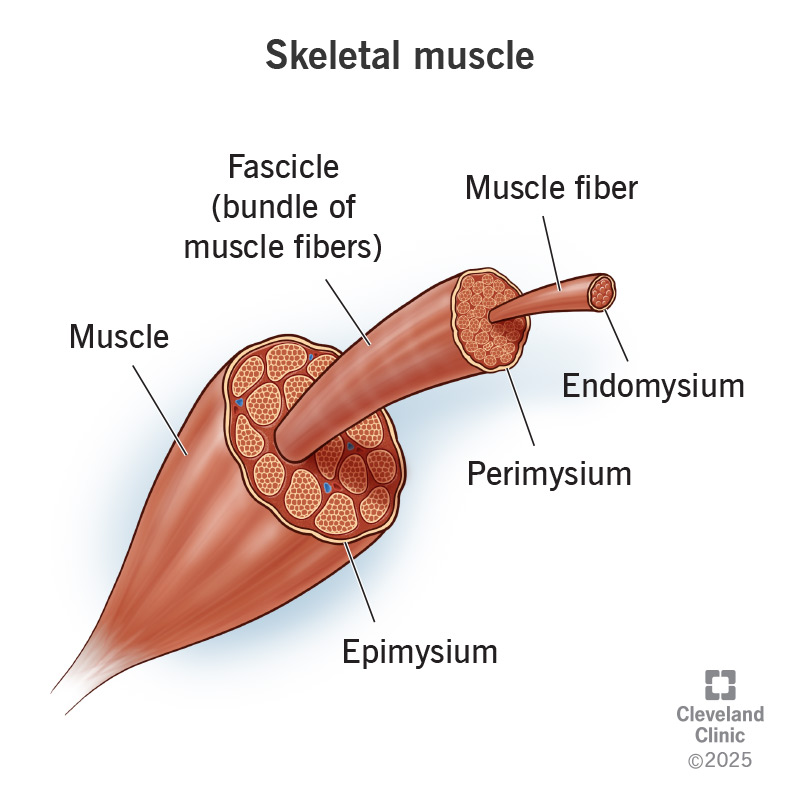
Your skeletal muscles are located between the bones (skeletal system) throughout your body. They consist of flexible muscle fibers that range from less than half an inch to just over 3 inches in diameter. These fibers usually span the length of the muscle. The fibers contract (tighten), which allows the muscles to move bones so you can perform lots of different movements.
Each muscle can contain thousands of fibers. Different types of sheaths, or coverings, surround the fibers:
Skeletal muscle fibers are red and white. They look striated, or striped, so they’re often called striated muscles. Cardiac muscles are also striated, but smooth muscles aren’t.
A wide range of conditions can affect skeletal muscles, from mild injuries to serious or even life-threatening myopathies (diseases that affect skeletal muscles). A few are:
Skeletal muscles (striated muscles) are the most common muscles in your body. You use them to breathe, eat and move your bones, so they play a vital role in everyday activities. Therefore, it’s important to keep your muscles as strong and healthy as possible. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to build and maintain muscle strength, which can affect your overall health.
Advertisement
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.

Last reviewed on 04/14/2025.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.