Mesothelioma is a rare cancer that most commonly starts in the lining around your lungs. It can also start in the lining or sac around your abdomen, heart or testicles. Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough, night sweats, chest pain and digestive issues. Treatments include immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy and surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Mesothelioma is a rare cancer that can form in the lining around your lungs (pleura) or abdominal organs (peritoneum). Rarely, mesothelioma affects the sac around your heart (pericardium) or lining around your testicles (tunica vaginalis).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Mesothelioma starts in your mesothelium, a type of tissue that makes up a lining that surrounds and protects certain organs. It often creates multiple tumors that can sometimes combine into a sheet over the affected organs, making it hard to treat.
The most common type of mesothelioma is pleural mesothelioma, which affects the lining of your lungs. Other types include:
Sometimes, solitary fibrous tumors are called “benign mesothelioma,” but they’re not really related to cancerous (malignant) mesothelioma.
You might also hear mesothelioma described as epithelioid, sarcomatoid or biphasic (a mix of both). This describes the shape and other characteristics of the cancerous cells. The type of mesothelioma you have might affect your treatment options and prognosis (outlook).
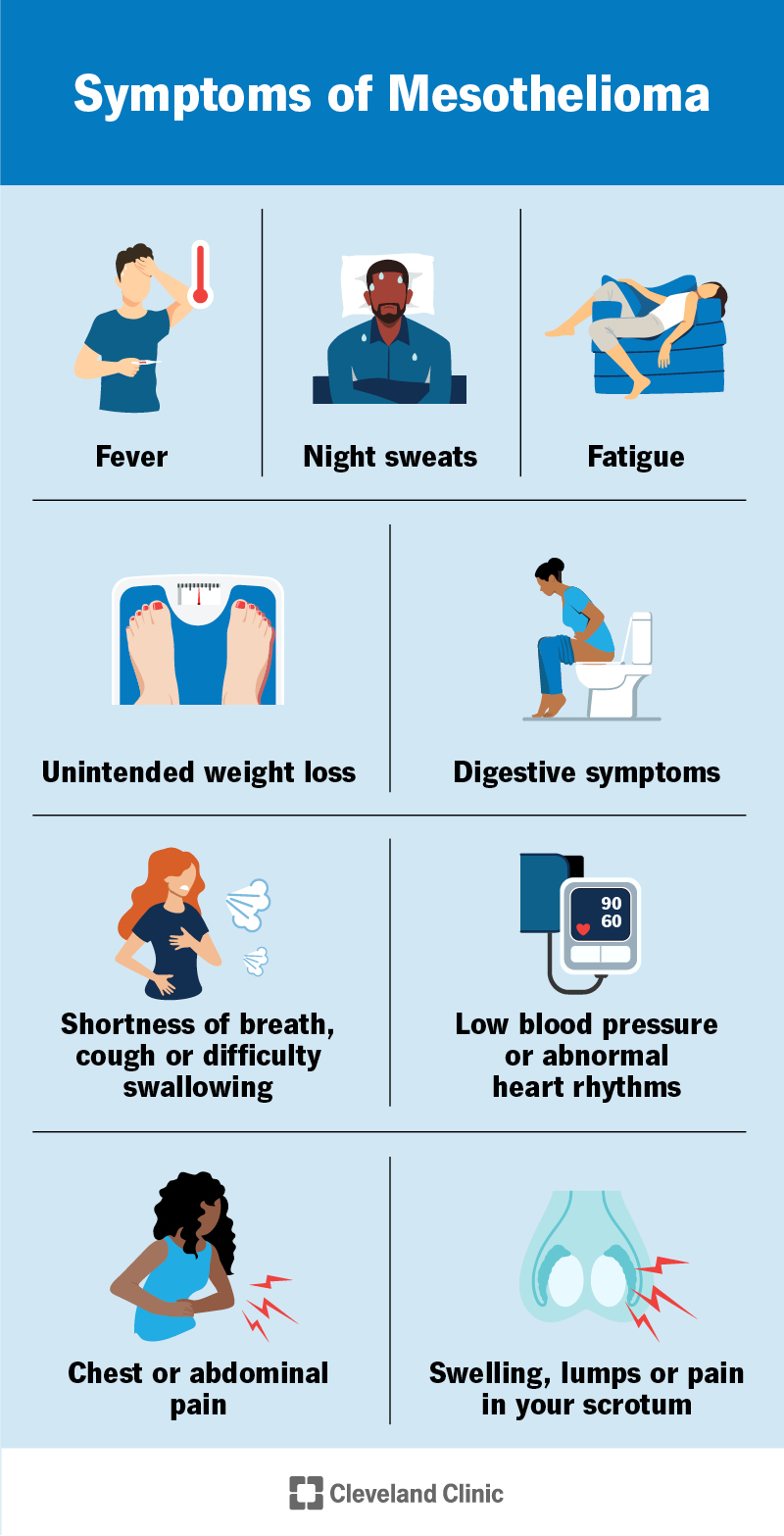
Symptoms of mesothelioma depend on where it is in your body. They include:
Advertisement
Asbestos exposure is the most common cause of mesothelioma. Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral once commonly used in many industries, including construction, shipbuilding and the automotive industry. It has needlelike fibers that can damage your tissues if you breathe them in or swallow them. Mesothelioma doesn’t show up right away — it can take decades for cancer to develop after asbestos exposure.
But developing cancer can depend on many factors — most people exposed to asbestos don’t get mesothelioma. And people with mesothelioma don’t always have a history of asbestos exposure.
Having a job that exposed you to asbestos is a risk factor for mesothelioma. These could include:
Other risk factors include:
Mesothelioma can spread (metastasize) to other parts of your body. It can also cause fluid to build up around your lungs (pleural effusion) or heart (pericardial effusion) or in your abdomen (ascites).
Based on your symptoms and health history, your provider might get the following tests to diagnose or rule out mesothelioma:
Typically, no single treatment can cure mesothelioma on its own. Treatment options for mesothelioma depend on the kind you have. Options could include:
Advertisement
Talk to your provider if you notice symptoms like shortness of breath, persistent cough or changes in your bathroom habits. It might seem scary to investigate your symptoms, but getting treated early is always better than waiting.
Survival rates for mesothelioma depend on the kind you have. For example, the five-year relative survival rate for the most common type, pleural mesothelioma, is between 7% and 24%. In general, peritoneal mesothelioma survival rates are higher than those of other types.
Keep in mind that these numbers are based on people diagnosed at least five years ago. They may not reflect what you can expect with new treatments or other factors of your specific situation. Ask your provider what to expect.
No, mesothelioma isn’t fatal for everyone. But it’s an aggressive cancer that’s rarely caught in early stages, when it’s more treatable.
Cancer is rarely completely preventable. You can reduce your risk of mesothelioma by avoiding asbestos. Take precautions for proper handling and disposal if you have to work with it or around it.
If you had a job that exposed you to asbestos in the past, talk to your provider about whether they have recommendations for monitoring or screening for potential health issues.
Advertisement
A mesothelioma diagnosis can come with a lot of worry and uncertainty. It’s natural to want to know what lies ahead and a clear path to follow. It might be helpful to find support groups and other resources that can offer support and help you understand your options. Have honest conversations with your provider about your specific situation, your concerns and what to expect.
Advertisement
No matter if you need drug therapy, radiation or surgery (or all three), our mesothelioma treatment focuses on your needs and goals.

Last reviewed on 04/18/2025.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.